Amid a surge in COVID-19 cases, you might have heard the term ‘CT value’ or ‘CT count’ floating around. CT value threshold helps to identify whether a patient is COVID positive or not. Here is everything you need to know about the CT count of a COVID test.
What is CT value or CT count?

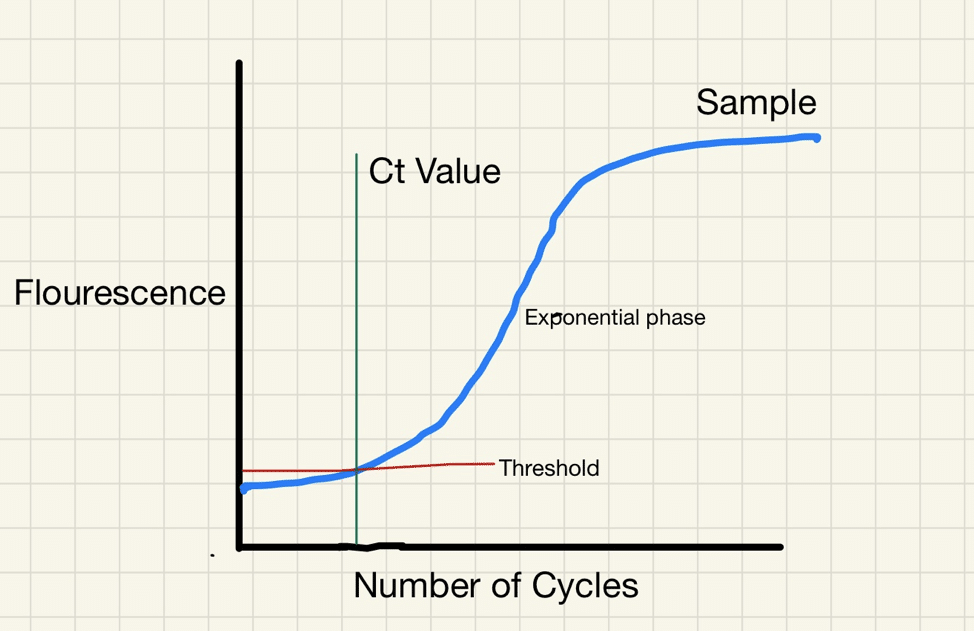
CT count or cycle threshold is the number of cycles required to amplify viral RNA to make it detectable. In simple words, the CT value determines the viral load in the body.
Why is CT count important?
According to the American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC), an individual is considered COVID-19 negative, if the CT value is 35 or above in the RT-PCR test. So, if the CT value is below 35 in the RT-PCR test, then the patient is coronavirus positive.
Lower CT value – Higher viral load
Higher CT value – Lower viral load
Which COVID-19 test gives the CT count?

The three most common types of COVID-19 tests are molecular (like RT-PCR), antibody, and antigen tests.
Molecular tests detect the viral genetic material from the patient’s swab sample. It gives the CT count.
On the other hand, an antigen test can detect viral proteins collected from a swab test. The antibody or serological tests detect antibodies against COVID-19 in the patient’s blood sample.
What is RT-PCR?
Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) test helps in ‘seeing’ the virus. Here’s how:
First, it extracts the viral RNA from the sample. It undergoes a reaction with a reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Viruses have RNA as genetic material. So, the enzyme helps in transcribing the viral RNA into DNA.
A complementing template is created and reacted with the DNA. Many primers help in binding it to the transcribed DNA.
Small primers add up to build DNA. Multiple copies of the resulting DNA sequence are created- in a chain reaction.
Those DNAs are measured when passed through fluorescence (light).
How is CT count measured?
DNA calculated from RT-PCR determines the CT count. A lower CT count shows a high viral load. Why? Because this means that fewer reaction cycles took place to show the viral genetic material.
CT count is an important factor in determining the coronavirus in the body. It does not relate to the severity of the disease. However, it determines the presence of the disease. Research on the connection between CT counts and the worsening of COVID symptoms is in progress.





