
Chinese authorities began mass testing for coronavirus in Wuhan as a result of series of COVID-19 outbreaks in and around the city. The disease first originated in the city in late 2019.
Citywide testing after multiple COVID-19 outbreaks
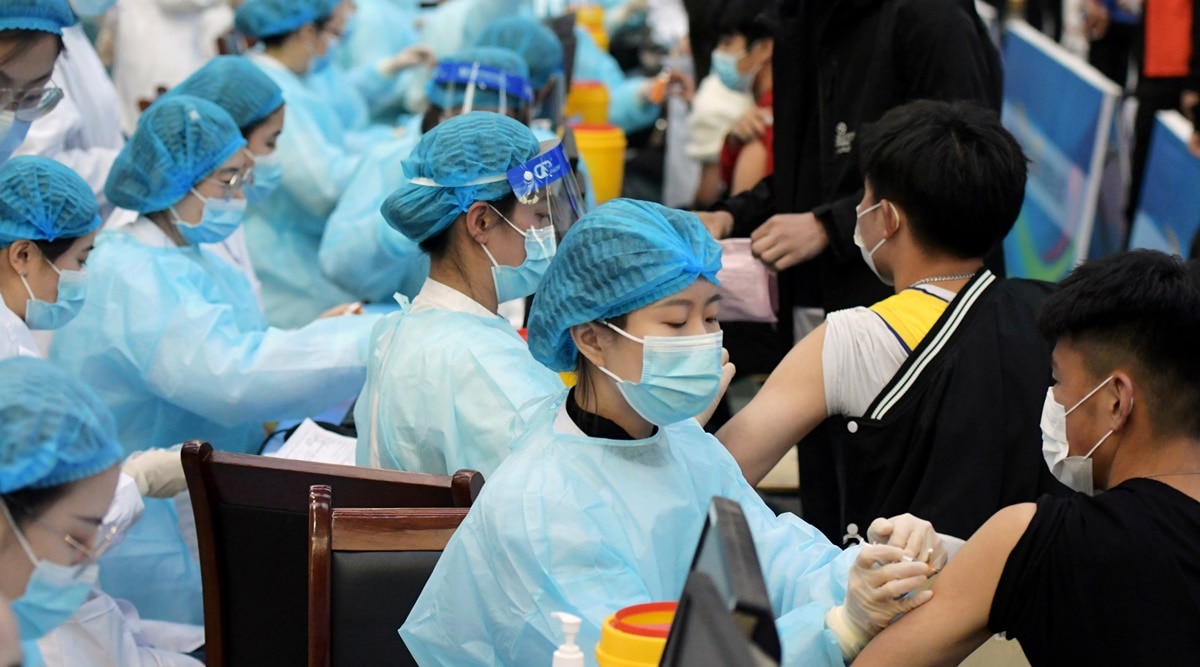
Wuhan is the largest city in China to undergo mass city-wide testing. The city recorded three non-imported cases for the first time on Monday. With a population of 11 million, the city is the provincial capital in central China. The country has been successful in curbing the virus after a devastating initial outbreak. However, since then, the Chinese government has reduced testing. It also focused on controlling the disease when a new case popped up with mass testing, isolation, and speedy diagnosis.
The current COVID-19 outbreaks in China are totaling around 100 cases. But, they have spread widely in comparison with the previous waves. The outbreak, reaching over multiple cities and provinces is of the highly contagious delta variant.
New cases and the need for new solutions
“90 new cases had been confirmed the previous day. 61 locally spread ones and 29 among people who had recently arrived from abroad,” stated the National Health Commission of China. Additionally, most of these new cases are in the Jiangsu province where an outbreak occurred at Nanjing airport. The outbreak has been spreading and reached the city of Yangzhou, 35 miles from Nanjing.
Moreover, five other provinces of China reported local cases. However, as of now, they are in single digits. A driver working in Shangai airport tested positive Beijing alone has a total of five new local cases. According to the scientists from the Government-affiliated research institute, the Chinese vaccines are not very efficient against the new variant. But, they offer low protection. The vaccine is only available in China. According to the authorities, over 1.6 billion doses are administered.
